VSAT - VERY SMALL APERTURE TERMINAL
A very small aperture terminal (VSAT), is a two-way satellite ground station or a stabilized maritime VSAT antenna with a dish antenna that is smaller than 3 meters. The majority of VSAT antennas range from 75 cm to 1.2 m. Data rates typically range from 4 kbit/s up to 16 Mbit/s. VSATs access satellite(s) in geosynchronous orbit to relay data from small remote earth stations (terminals) to other terminals (in mesh topology) or master earth station "hubs" (in star topology).
A VSAT network typically consists of a larger earth station, commonly referred to as a teleport, with hub equipment at one end and a Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT ) antenna with remote equipment at the other end. The network equipment can be divided into two sets of equipment connected by a pair of cables: the Outdoor Unit (ODU) and the Indoor Unit (IDU).
A VSAT network typically consists of a larger earth station, commonly referred to as a teleport, with hub equipment at one end and a Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT ) antenna with remote equipment at the other end. The network equipment can be divided into two sets of equipment connected by a pair of cables: the Outdoor Unit (ODU) and the Indoor Unit (IDU).
ODU
An ODU is the equipment located outside of a building and includes the
satellite antenna or dish, a low noise block converter (LNB), and a
block-up-converter (BUC). The LNB converter amplifies the received signal and
down converts the satellite signal to the L band (950 MHz to 1550 MHz), while
the BUC amplifies the uplink transmission when the antenna is transmitting.
IDU
The IDU equipment at the teleport usually consists of a rack-mounted hub system and networking equipment connected to terrestrial networks, like the PSTN or Internet backbone. There is also a device that converts between satellite and IP protocols for local LAN applications such as PCs, voice calls and video conferencing.
The IDU equipment at the teleport usually consists of a rack-mounted hub system and networking equipment connected to terrestrial networks, like the PSTN or Internet backbone. There is also a device that converts between satellite and IP protocols for local LAN applications such as PCs, voice calls and video conferencing.
At the remote location, a router
connects to a small VSAT antenna receiving the IP transmission from the hub
over the satellite and converts it into real applications like Internet, VoIP
and data.
Topologies
Network topologies define how remote locations connect to each other and to the hub. The link over the satellite from the hub to the remote is called the outbound or downlink transmission, whereas the link from the remote to the hub is referred to as inbound or uplink.
Network topologies define how remote locations connect to each other and to the hub. The link over the satellite from the hub to the remote is called the outbound or downlink transmission, whereas the link from the remote to the hub is referred to as inbound or uplink.
Satellite networks are primarily
configured in one of these topologies:
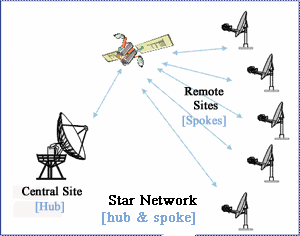
Star (hub & spoke) Networks
In a star network topology the hub connects to the remote, where all communications are passed back through the hub. Virtually an unlimited number of remotes can be connected to the hub in this topology. Smaller, lower powered BUCs can be used at the remote end since they are only connecting back to the larger hub antenna.
Star (hub & spoke) Networks
In a star network topology the hub connects to the remote, where all communications are passed back through the hub. Virtually an unlimited number of remotes can be connected to the hub in this topology. Smaller, lower powered BUCs can be used at the remote end since they are only connecting back to the larger hub antenna.
Mesh Networks
A mesh network topology allows one remote VSAT location to communicate with another remote location without routing through the hub. This type of connection minimizes delay and often is used for very high quality voice and video conferencing applications.
A mesh network topology allows one remote VSAT location to communicate with another remote location without routing through the hub. This type of connection minimizes delay and often is used for very high quality voice and video conferencing applications.
With this topology, larger antennas
are required and more power is needed to transmit, thereby increasing cost.
Hybrid Networks
A hybrid topology is a mix of star and mesh networking solutions. This topology allows the hub to send information to the remotes, with the remotes then able to communicate with other VSAT locations.
A hybrid topology is a mix of star and mesh networking solutions. This topology allows the hub to send information to the remotes, with the remotes then able to communicate with other VSAT locations.
Point to Point Connectivity
Contrary to the networking topologies, a point-to-point topology involves a dedicated connection between two antennas. This topology is a direct pipeline with a set bandwidth capacity regardless of usage and is typically designed with Single Carrier per Channel (SCPC) technology.
Contrary to the networking topologies, a point-to-point topology involves a dedicated connection between two antennas. This topology is a direct pipeline with a set bandwidth capacity regardless of usage and is typically designed with Single Carrier per Channel (SCPC) technology.
Thanks for post! VSAT network. VSAT network
ReplyDelete